From Fresh to Secure
Tutorial: Securing a Platform from Scratch: Step-by-Step Guide
This tutorial walks you through securing your embedded platform from a fresh system install, using the RidgeRun Platform Security Manual as a reference.
A secure platform follows a similar structure to the following:
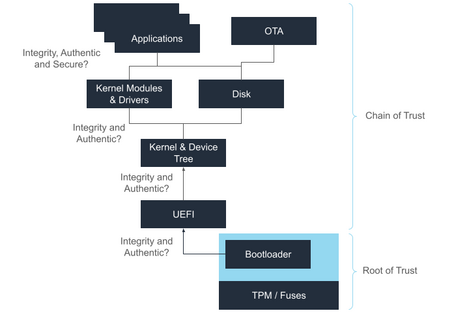
1. Understand the Security Fundamentals
Before implementation, ensure you're familiar with the building blocks of platform security:
- Root of Trust (RoT): Establishes a trusted base for system validation.
- Secure Boot: Ensures only signed, verified code runs at boot.
- Trusted Execution Environment (TEE): Isolates sensitive operations in a secure CPU region.
- Disk Encryption: Keeps data secure at rest.
- Over-the-Air Updates: Keeps the system updated.
For more information on the fundamentals, please, check the Platform Security section.
2. Implement Secure Boot
Secure Boot involves a series the steps. It can be considered the longest process when preparing a secure platform. Nevertheless, ensuring secure boot prevents the system from loading software components which have been altered or come from untrusted sources.
The following steps are required for NVIDIA Jetson:
- Generate cryptographic key pairs: it involves creating certificates and generating keys.
- Burn public key hashes into fuses (irreversible): it involves the use of the Factory Secure Key and Expansion Key Provisioning (FSKP) from NVIDIA and burning the fuses.
- Sign bootloaders and OS components with your private key: it involves signing the bootloader, kernel and device tree.
- Activating UEFI Secure Boot: involving the generation of the UEFI keys and the UEFI payloads.
- Flashing: transferring the OS components to the board.
3. Set Up a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE)
TEE Overview and Setup
- Compile OP-TEE modules and device tree: enabling OP-TEE allows critical security components to work, from disk encryption to customer's secure apps.
- Integrate it into the build: flashing the board with the new device tree and modules.
It provides a hardware-backed, isolated environment for secure operations.
4. Enable Disk Encryption
NVIDIA Jetson Disk Encryption Setup
- Install tools like
cryptsetup. - Define encrypted partitions (rootfs, data, etc.).
- Generate and securely manage encryption keys.
This ensures your stored data is protected even if the device is compromised.
5. Implement Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
OTA Security Guide
- Choose and integrate an OTA system (e.g., Mender).
- Ensure it supports authentication, rollback, and verification.
- Integrate with Secure Boot and TEE to maintain trust throughout the update process.
6. Add Additional Security Layers
Platform Security Extensions
- Implement Trusted Platform Module (TPM) if hardware supports it.
- Use a secure key management system (e.g., kernel keyring).
- Apply IMA (Integrity Measurement Architecture) for file integrity checking.
7. Test and Validate Your Security Setup
- Verify Secure Boot with unauthorized code tests.
- Test TEE applications and ensure isolation.
- Confirm encryption works by examining partition data externally.
- Simulate OTA updates to verify rollback and signature validation.
For detailed instructions and platform-specific steps, refer to the full RidgeRun Platform Security Manual.



